Unit 12 A Health Body
Topic
Measuring lung capacity
Curriculum Link
12.9 Exercise and Health
Estimated Lesson Time
80 minutes
Introduction
Students are engaged to attend to the importance of lung capacity by watching a video clip 'Free-diving'. Then they are required to complete three tasks in this learning activity. Firstly, they conduct an experiment to measure their lung capacities. Then teacher provides students with opportunities to elaborate the concept of lung capacity in relating to some sports. Finally, students are invited to suggest methods to measure the strength of their lungs.
Key Question
How strong is your lung?
Learning Objectives
In this activity, the students should be able to
- understand lung capacity as an indicator of fitness;
- observe, measure & record data during experiment (SP1);
- draw conclusion from the data collected (SP5);
- suggest methods to measure the strength of their lung.
Teaching Plan
| Task (Time) | Brief Description | Materials | Objectives |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Engagement |
Teacher shows a video clip 'World Record of Free-diving' to students. Teacher could explain 'Free-diving' as 'diving without oxygen kit' and invite students to guess how deep the diver could push underwater https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vF4PN8-2YSk
Teacher could engage students to attend to the relationship between lung capacity and air pressure by asking:
|
(1) | |
Exploration |
Students explore their lung capacity by task 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cy4kzOeLD5E
|
|
(1) & (2) |
Explanation |
Teacher explains the principle of measuring lung capacity.
|
(3) | |
Evaluation |
Students' understanding of lung capacity is evaluated by asking students to complete Task 1 questions:
(Optional) Ask students to suggest methods to improve the above experiment. |
||
Elaboration |
Students elaborate the concept of lung capacity in relating to some sports in Task 2 'Which people have strong lung capacity? Explain their answers?' (Optional for the following discussion)
|
(1) | |
Exploration |
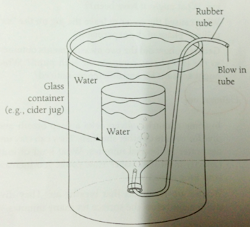
Teacher demonstrates a simple method below to measure the strength of lung. Students are invited to suggest methods in task 3. Suggestions to determine the strength of lung :
|
|
(4) |
*Apparatus and materials required:
- 5L Gas bottle
- Large plastic container for water
- 6 Rubber tubing, 5 mm inside diameter, and 30 cm in length
- Few mL of alcohol for disinfectant
- Plastic bag
- Tissue
- Book